

  |
The Ribat National
University
Khartoum, Sudan
Introduction
:
Computer crime, sometimes referred to as cyber crime, is becoming the biggest challenge to the modern societies. In the developed countries the biggest challenge that face law enforcement is the crimes committed using computer technology. Computer crime can be divided into two categories :
a) Crimes in which computer is used as a tool to aid criminal activity such as producing false identifications, reproducing copyright materials, and many other things.
b) Crimes in which computer is used as a target, and probably a tool, to attack organizations in order to steal or damage information, attack banks to make unauthorized money transactions, steal credit card numbers, and many other activities.
According to Computer Security Institute 85% of large corporations and government agencies in the US detected computer security breaches during the year 2001. 64% of them suffered from financial loses due to computer breaches. 95% of these corporations and agencies detected computer viruses. The same source reported that there were 25,000 attempted intrusion into the US defense system during the same year, out of this number 245 attempts were successful. In order to face this problem, which is increasing every day, president Bush allocated $4 billion in the 2002 budget for information systems security (Lemos, Robert 2002).
Computer Viruses
:
The 2000 computer virus prevalence survey reported 10 billion Dollars damage estimate from computer viruses. The BBC World News in the 8th of June 2000 reported that the love virus affected more than 45 million computers and according to Lyman, among these were the computers of the Pentagon, the CIA, and the British Parliament. The damage of this virus according to the same source reached 8.75 billion Dollars.
The Cooperative Association for Internet Data Analysis (CAIDA) reported that code red worm affected more than 359,000 servers in less than 14 hours.
Hackers :
The term hackers is used for people who gain illegal access to other people’s systems. The term hacker was originally associated with outstanding and radical programmers in computer science fields (usually from Barkley, Stanford, or MIT), Chandler 1996.
According to High-Tech Dictionary a Hacker is one who is knowledgeable about computers and creative in computer programming usually implementing the ability to program in Assembly Language or low-level language.
A hacker can mean an expert programmer who finds special links for getting around obstacles and stretching limits of system.
The term carried different meanings through four generations.
1st generation (1960s) Used the term for a creative programmer
2nd generation (1970s) Used the term for computer evolutionaries.
3rd generation (1980s) Used the term for games and copyright breakers.
4th generation (1990 to date) Used the term for criminal and cyber criminal.
The term is defined in Merriam Webster Dictionary as “a person who illegally gains access to and sometimes tampers with information in a computer system”.
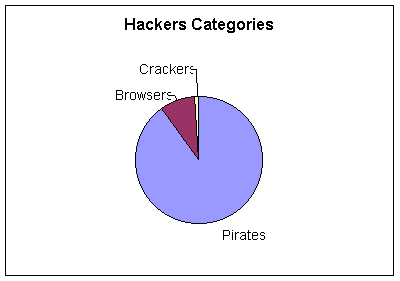
Hackers has been divided in several categories :
a) The amateur group who are the least technically proficient and confined their activities to prove their capability of penetrating systems.
b) The browser group has moderate technical ability and gained unauthorized access to other people’s files They might violate copyright but they do not damage files.
c) The cracker group (cyber criminals) who has the most technical ability. They are the most dangerous group and the most serious abusers. Their activity ranges from copying files to damaging programs and systems.
d) According to the IBM global security analysis lab there are about 100,000 hackers world wide.
90% of these hackers are from the first group (pirate group).
9% are from the second group (browsers), and not more than 1% are from the third and most dangerous group. Hackers see security systems as challenge, not an obstacle.
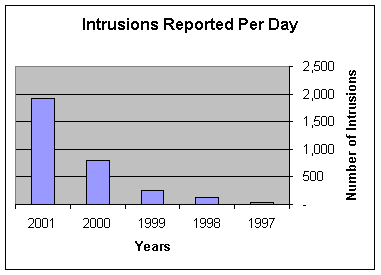
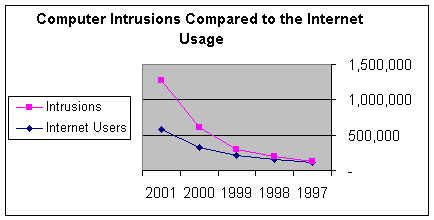
The latest internet statistics in the web-police site indicated that in the year 2001 there were 5,700,000 intrusions done by hackers. 12% of these intrusions caused damage.
80% of these intrusions were done by insider hackers and 20% by outsider hackers. These intrusions cost about 5.5 Billion Dollars in stolen software and 1 Billion Dollar in stolen telephone credit cards. The rate of increase in these crime is growing very quickly according to the following table:
The
Year Reported Intrusions Average
Per Day
1997 12,775 35
1998 47,614 130
1999 94,791 258
2000 289,303 793
2001 701,939 1923
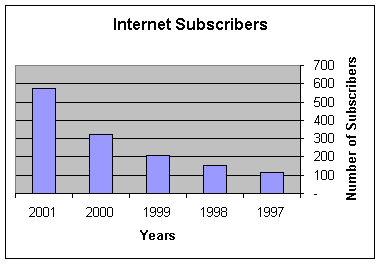
The web users according to the same statistics are as follows:
1997 117 Million
1998 151 Million
1999 206 Million
2000 322 Million
2001 574 Million
46% of these users are in the Unite States of America and 54% are in the rest of the world.
How do They Hide
the Evidence ?
Criminals use several methods to hide their crime and to make it very difficult to trace their activity. Some of these methods are :
Encryption :
Many of computer criminals tend to encrypt their messages, whether it is voice or text message, to make their communication inaccessible to law enforcement. The FBI was unable to decrypt many communication intercepts in the past years according to its director Louis J. Freeh. They usually conduct encrypted voice conversations through the internet relay chat (IRC) at very little or no cost.
Encrypted e-mail :
Hackers encrypt their e-mail messages. Most of them use Pretty Good Privacy software (PGP) to encrypt their messages. This software is could be downloaded from the internet for free. Hamas used encrypted internet messages and communications to transmit maps, pictures, and other details to different locations.
Multiple Encryption :
The well known hacker Kevin Poulsen encrypted his files more than once using defense encryption standards. To break his codes a super computer was operated for several months which cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Passwords :
Locking the files with passwords is much more used by cracker than encryption.
Compressing Files :
Compressed files are more difficult to access in addition to the advantage that when compression is done before encryption it makes it more difficult for cracking.
Steganography :
This technique is hiding the secret data inside other files such as image files, sound files, or video files. The secret data can also be hidden in the unallocated sectors of a disk. This data become invisible for any one who does not know the filename and the password. The size of the secret data might be bigger than the image file but still it could be put inside it without noticing any change in the image file size. Performing this technique is very easy. You do not have to do anything other than drag the data file and put it on the image file. The tools for this technique are called S-Tools and could be downloaded from the internet for free.
Remote Storage :
Hackers can store data on remote hosts, if they find a poor security measures in this systems, without the knowledge of the owners of these hosting systems. Sometimes it might be the server of the ISP.
A group of hackers from the Netherlands broke into the system of the Defense Department and stored the stolen data in hidden folders into the system of University of Chicago in order to transfer it later on to different location.
Anonymous mailing :
Anonymous mailing is sending a message to the destination without any information about the sender so that the receiver will not be able to know the sender or the source of the message. This technique could be done using what is called anonymous remailer which is a mailing service that allow some one to send an e-mail without the receiver knowing who the sender is. Some remailers keep enough information about the sender to enable the receiver to reply to the sender through the remailer. Others offer full anonymity and do not support any reply service. Some remailers provide encryption service.
Some hackers send their messages through multiple remailers to make it very complicated for tracing like the death threat which was sent to president Clinton.
Using Open Forum :
Criminals can communicate freely on open forum using encryption techniques. This was done by those who threatened to kill Microsoft president Bill Gates in 1997. They used America Online Netgirl Bulletin Board. The threat was traced to Adam Quinn in Long Grove, Illinois.
Computer Penetration and Looping :
Hackers can penetrate a computer system and use it as spring board to jump to a second and a third system before sending their message to make it difficult for investigators to trace. This technique is called looping.
Audit
disabling :
Some organizations has a software that keep the logging activities on the system in order to be traced back in case of incidents. Criminals could disable the auditory part in this software or delete the records pertaining their activity using some other software such as Root Kit or Zap. (Both of these could be downloaded from the internet).
References
:
Abreu, Elinor Mills 2002 : US Firms Announce New Security Technology,
www.dailynew.yahoo.com, Sat. 23/2/2002
Andamski, A. 1999: Crimes Related to the Computer Network, Threats and Opportunities. A criminological perspective.
CERT Coordination Center, How FBI investigates computer crime,
Chandler, N. 1996 : Profile of a Computer hacker.
Florida : infowar.
Denning, Dorothy E. and Baugh, William E. Jr. 1999 : Hiding crime in Cyber space,
Information, Communication and Society : Vol. 2, No.3, Autumn 1999.
IBM global security analysis lab,
York Town Heights, New York.
International Web Police, Latest internet statistics,
Lemos, Robert 2002 : Security Confab Call for US Spending,
www.news.com, 21/2/2002
Lyman, Jay 2002 : In Search of theWorld’s Costliest Computer Virus,
www.newsfactor.com, Thur., 21/2/2002
Parker, D.1998 : Fighting computer crime : A new frame-work for protecting information.
JohnWiley & Sons Inc., New York
Rogers, Marc 1999 : New hacker taxonomy,
University of Manitoba
Rogers, Marc 2000 : Security threats,
University of Manitoba
Latest internet statistics,
Weisman, Robyn 2002 : US Security Holes : Don’t Blame Technology,
News Factor Network, 19/2/2002